
Not 100% true (floppy discs or zip drives anyone?), but I like the thought.

Not 100% true (floppy discs or zip drives anyone?), but I like the thought.

I’m having a clearout of my office and I keep stumbling on various things. Here’s the cover from someting I did 10 years ago, along with a list of 10 trends for 2010. They seem pretty on the ball for 2020. Someone once said that I’m 10-years ahead of everyone else, which perhaps could be read as meaning that anything I say now can’t be assessed, or isn’t meaningful, until 2030.


I cannot wait to re-read this little lot and work out what they got right, what they got wrong and possibly why. The World in 2020 (top) was written in 1994, Horizons 2020 (Siemans) in 2004 , Future Agenda 2020 (Vodafone) in 2010 and Futrecast 2020 in 2008.

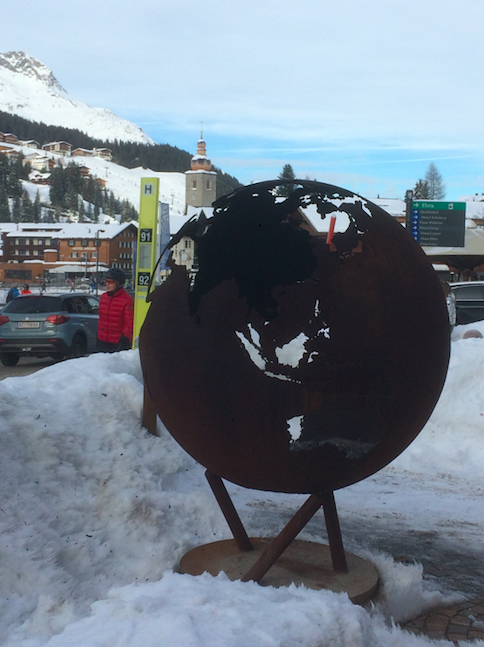
I should perhaps point out that this isn’t photoshop, it’s an actual fire globe in Austria. Can’t help but think that Sydney fireworks missed a trick. Perhaps they should have asked everyone around the harbour to simply turn they phone flash lights on instead and given the cost of the fireworks to the rural fire service.

Following on from my Table of 100 Disruptive Technologies, I recently received an enthusiastic email from Max Nocerino, a Sci-Fi fan and aspiring futurist from Queens, New York. His idea is a table of future tech, but one that’s very much in the Twilight Zone, to borrow a Sci-fi reference. In other words, tech that’s highly improbable, but hugely impactful were someone able to figure out how to do it. Clearly some of these ideas will be ‘impossible’ given today’s science, but remember the Earth was once thought to be flat and about 6,000 years-old, so perhaps our understanding of most things can change given enough time. His first entry is Faster Than Light Travel, an idea I myself had on a Future of Space graphic recently.
Max’s explanation below, along with some detail from the Future of Space.
“This has been something that has been depicted in sci-fi since the beginning of time. Our first Moonshot is Faster than light travel; but is it possible? Many sci-fi mediums have depicted a parallel dimension called ‘Hyperspace’ that allows a ship to move many times faster than light and reach other Star systems in mere hours instead of thousands of years. The Millennium Falcon from Star Wars can travel at a little over than the equivalent of 4 quadrillion miles per hour and can reach another galaxy in roughly 100 days. Even if we could move at the speed of light; it would still take us 4 years to reach the nearest solar system, Alpha Centurai.
So how do we achieve this since we don’t know if ‘hyperspace’ exists and even if we did; we don’t know how to access this dimension. In 1994, Mexican physicist Miguel Alcubierre envisioned what was eponymously called the Alcubierre Drive, in which a ship could create a warp bubble around a ship that would fold space in a sense and make the distance between the vast void between stars, much smaller.
Another option would be to travel in through a wormhole like in the sci fi movie Interstellar. A wormhole is a hypothetical singularity Point in space that connects two points in space time and would allow a ship to be connected to another region instantaneously. Unfortunately, wormholes (if they exist) may only exist for seconds and may not be big enough for a ship to fit into. There is also now new evidence that even if this is possible; travel through one would still be slow. My personal idea for FTL would be to heat something to absolute hot or the Planck temperature where the laws of physics no longer apply and then the ship could pass through the vacuum since the expansion of the universe; the fabric of space time DOES move FTL. A ship would need a way to generate this intense heat and then shield itself from the heat (perhaps with a deflector shield). This is all speculation but since the universe itself moved faster than light at the point of the Big Bang; it is a possible phenomenon. We just need to figure out how to initiate it naturally….”
—
BTW, for further context: “When a distinguished but elderly scientist states that something is possible, he is almost certainly right. When he states that something is impossible, he is very probably wrong.” Arthur C. Clarke.

Maybe that’s a bit over the top, but I just love this idea. The Resturant of Order Mistakes is a restaurant in the Toyosu district of Japan that is staffed by people with dementia and Alzheimer’s. The idea is to show that people with these conditions can be productive members of Japanese society (which, by the way, is ageing faster than any other country on Earth and gives us a foretaste of what many other societies will face in the future).
As you might imagine, customers do not always get what they ordered — but very few people complain. If nothing else, the idea teachers people to be patient and forgiving.
The restaurant is a twist on a 1924 Japanese story called The Restaurant of many Orders.
What a lovely thing to do. 2-minute video here.
(Thanks to Jules for this, btw).
I don’t remember where I heard this (I may even have read it in a book I’m reading called The Geography of Genius), but someone recently said that the golden age of den (camp) building was between the wars. I disagree, I think it was post WW2 and, in particular, in the 1960s before urban development went into overdrive. My own personal experience was camp building in the late 60s and early 70s when many of the bomb sites from WW2 were still vacant land. The big houses had generally been cleared, but the land had not, which meant I had acres of wild space on my doorstep. Probably trespassing, but nobody seemed to care back then. We dig huge holes, made bows and arrows , built fires and constructed camps.
So, my question is this. If the 50s, 60s , 70s or whatever were indeed the peak of den building (and generally of kids, especially boys, running wild outside), did this have a lasting effect on the imaginations of these generations? More to the point, given that kids generally play indoors nowadays, what is happening to their imaginations today? I’ve seen a study saying that creativity among kids started to decline roughly when video gaming and cable TV started to become popular and another study saying that the distance kids roam around their home has shrink considerably over the last few decades, especially since the dawn of the internet and social media, so maybe so? Or maybe kids just build things and roam around in VR rather than RL these days?
BTW, if you Google golden age of den, or camp, building you get zip, which means there could be something to be written about this. But not by me.
Book link here that’s vaguely connected.
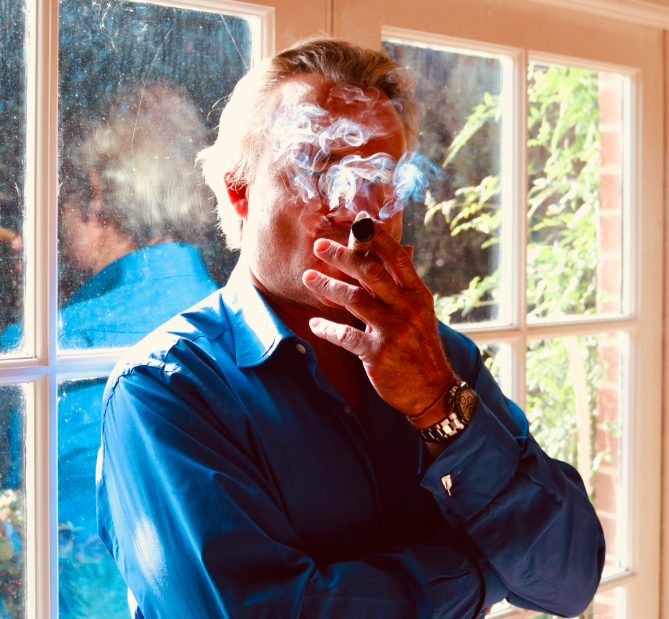

Historically, the sight of rising smoke generally meant human activity or presence. To some extent it symbolised life. Nowadays it generally means the opposite. Smoking is deemed bad for us. It is bad for the environment too. Puffs from cigarettes have more or less been outlawed, replaced with clouds of electronically generated vapour.
A microwave oven probably produces more pleasure than these dreadful devices, which seem to have more in common with mobile telephones and their chargers than old-fashioned cigarettes.
What of cigars? Cigars are somewhat different. They are still an outlaw activity, but they have escaped the opprobrium of the pleasure censors, possibly because they are generally consumed behind closed doors. It is also a minority pursuit, so hardly worth the attention. But why smoke a cigar? More to the point, why do I?
I cannot explain why I started to become a cigar enthusiast, but I can perhaps explain why I haven’t stopped. In a nutshell, I see things more clearly through a haze of sensuous, swirling, cigar smoke.
I think it’s the breathing more than anything else. You have to really think about how and when you breathe. If you have ever tried meditation the parallels are not insignificant. You are fully present in the moment. I wouldn’t go so far as to suggest that smoking cigars is healthy, but they do help me to relax. I’ve never been a cigarette smoker, but it seems that cigarettes operate in the opposite direction. The expression ‘a quick cigarette’ is no accident. A quick cigar, in contrast, is practically impossible.
It’s the smell too. I actually think cigars smell best before you light them. Annoyingly, they smell ever better when someone else is smoking one. Twin a cigar with a good malt whisky, or glass of cognac, and the pairing is almost incomparable. Somehow the smoke combines with the glass to create useful distortions of reality.
Cigars are also pleasing to look at and to hold in the hand too. And a hand-rolled cigar is human-made and always slightly different, which could perhaps be viewed as a revolutionary act of defiance against the cult of efficiency and homogenised societies that too often confuse fast movement with enduring progress.
The packaging of cigars is generally from a bygone era, as are many of the shops that sell them. This too is an example of how cigars, and the paraphernalia that surrounds them, is a welcome pause, or deceleration, from a world that is not only rapidly accelerating towards I have no idea what, but obsessed with immediate gratification, newness and novelty.
Another reason for smoking, or continuing to do so, is the complexity that surrounds the cigar. Like wine, there is a lot to learn about cigars and a lot of cigars to choose from. It is a complex and ritualistic world. To begin with this can be intimidating. (All I came out with from the very first cigar shop I visited, Davidoff in London, was a box of long matches). But the cigar world is full of people keen to share not only their knowledge, but their enthusiasm too. This is perhaps another parallel with the wine world. Eventually I settled upon a handful of favourite cigars, the Hoyo de Monterrey Epicure No.2, the H. Upman Magnum 46, the Romeo Y Julieta Short Churchill and the Bolivar No.2, but I continue to experiment.
There is also one further aspect, which, frankly, is not popular to discuss. This is the fact that cigar smoking is an almost entirely male activity. I have nothing against woman smoking cigars, in fact I rather like it, or perhaps I mean them. No, what I mean is that many of the rituals, meeting places and activities that were once wholly male have been invaded by women. Again, I have nothing against women, and nothing against places were both sexes might mingle happily, but just as women may need their own spaces so might men.
I will end by returning to my opening remark about thinking. How can it be possible for a cigar to make someone’s thinking clearer? The answer, in my experience, is that a cigar un-divides one’s attention. You start by cutting the cigar, carefully, and proceed to light it with expectant focus. The mind is already becoming unhurried. You take a puff (two puffs if the cigar is somewhat reluctant to fire up) and you see where the cigar takes you. You savour the flavour. You watch the smoke curl slowly upwards. Daily distractions momentarily disappear in the extended space between puffs. There is some solid science behind this, behind what appears to be nothing more than clouds of silent smoke.
When we are relaxed, when we are unhurried or seemingly wasting our time with empty moments, the mind starts to wander. As the writer and philosopher Alain de Botton once said: “The mind may be reluctant to think properly when thinking is all it is supposed to do.”
Given the right time and the right space the mind starts to seek patterns and connections in what we might ordinarily see as random inputs and experiences. You don’t always finish a cigar with an “ah ha” moment, but the very act of slowing down and sitting silently can do much of the groundwork to make insights and original thoughts rise to the surface. And, if none of this happens, you have at least had a relaxing moment to simply be.

In 1970, Alvin and Heidi Toffler wrote a book called Future Shock, which went on to become a worldwide bestseller. The core idea in the book was a condition characterised by “shattering stress and disorientation”, brought about by “too much change in too short a period of time.” I think they were 50 years ahead of the game!
I’ve contributed a small chapter to the book, which goes on sale at the start of February next year (4th Feb 2020). I’ll add some more posts on this in due course.
